Orthogonal LayoutDiscover concepts, use cases, and practical customization of the orthogonal layout
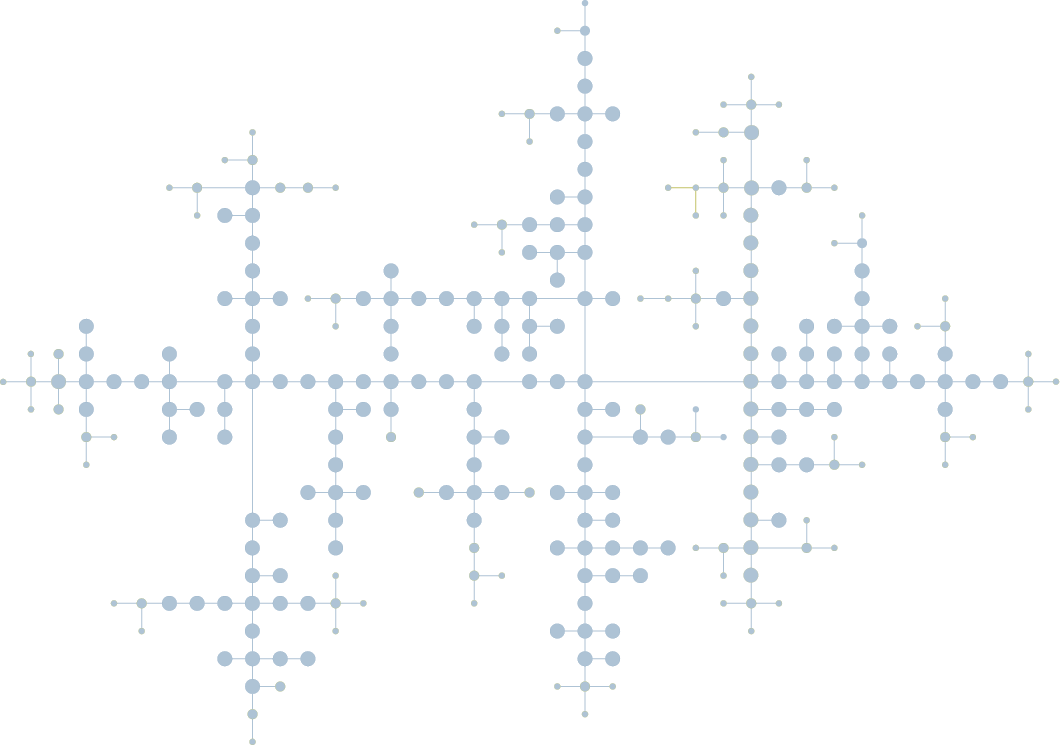
The orthogonal layout arranges graph elements so that all edges run exclusively at right angles, horizontally and vertically, to produce highly readable, grid-like diagrams. It’s ideal for software architecture, UML, circuit diagrams, database schemas, and other technical or structured data visualizations.

What is an orthogonal layout?
In graph visualization, orthogonal layout is a positioning algorithm that arranges nodes and edges so that all connections run exclusively at 90 degree angles (horizontally and vertically).
This creates grid-like diagrams that are particularly effective for things like visualizing code structures, control networks, and business processes.
Orthogonal layouts reduce visual noise by aligning data in a strict grid, making complex relationships easier to follow.
It works best when:
- You want right-angle connections
- Minimal edge crossings and bends are important
- A clear, grid-like structure improves readability

Create your own orthogonal diagram application
Whether you’re building UML class diagrams, circuit schematics, business process models, or custom technical visualizations: yFiles’ orthogonal layout arranges your data into clear, professional diagrams automatically—no manual alignment needed.
The advanced orthogonal layout algorithm instantly positions thousands of nodes and routes all edges at right angles, creating orderly, grid-based structures with minimal crossings and bends—even in large, interconnected networks.
Bring your diagrams to life with interactive features: rearrange nodes on the grid, highlight logical flows, auto-route connections, and enable seamless exploration of complex structures—on the web, in any framework, and on your preferred platform.
Build your first orthogonal graph application today—for free!
Start now
We´d love to help you. Reach out and we'll get in touch with you.
Your message has been sent.
Use casesReal-world applications of yFiles’ orthogonal layout in technical diagram visualization
From UML class diagrams and software architecture to electronic schematics and activity diagrams, orthogonal routing eliminates visual clutter and accurately represents relationships, dependencies, and logical flows.
UML class diagrams
By arranging nodes and edges exclusively along vertical and horizontal lines, the orthogonal layout keeps class relationships, inheritance chains, and interface implementations immediately clear—no matter the complexity of your code base.
In yFiles, orthogonal layout minimizes edge crossings and bends, aligning classes and their connections perfectly to a logical, grid-based framework. The result: class hierarchies and associations are presented in a clean, accessible format that accelerates code understanding and onboarding.

Flow and activity diagrams
Orthogonal layout excels at visualizing flowcharts, activity diagrams, and process workflows—types of diagrams where clear, direct flows and easy path-following are essential.
The layout makes process steps, control flows, and alternative branches easy to trace from start to finish. With yFiles, you can interactively build, update, and rearrange flow and activity diagrams. The orthogonal layout adapts instantly, keeping everything structured, readable, and aesthetically consistent—whether diagramming business processes, software logic, or organizational workflows.

CAD-like visualizations
Langner, Inc. uses yFiles’ orthogonal layout to visualize complex industrial control networks in a clear, CAD-style manner. This approach helps represent digital assets and their connections with right-angle edges, making diagrams familiar and easy to understand for users. The ability to minimize edge crossings and bends improves clarity and usability, which is crucial for cybersecurity risk assessment in critical infrastructure like power plants and factories. By integrating yFiles, Langner’s OTbase software offers fast, interactive network visualization with export options such as Visio, enhancing both security oversight and user adoption.
Langner, Inc. case study
Core principles of the orthogonal layoutTake control of structure and clarity
Grid placement
First of all, one of the key principles is that nodes are positioned on a grid. This sets orthogonal layout apart from other types, such as hierarchical layout, where node placement is more flexible. The grid-based positioning in orthogonal layouts enforces strict horizontal and vertical alignment, which helps maintain a clean and structured visual organization throughout the diagram.
Orthogonal layout operates on the basic assumption that both nodes and edge segments are placed on a grid. This introduces certain constraints, but also helps achieve a clean and structured layout. The layout algorithm aims not only to reduce the number of bends and crossings, but also to minimize the overall grid area used, resulting in a more compact drawing.

Kandinsky model
Another key assumption is the use of the Kandinsky model. In early scientific applications of orthogonal layouts, it was assumed that each node could have at most one edge per side, meaning a maximum of four incident edges. This was too limiting for many real-world use cases, where nodes often have higher degrees. The Kandinsky model addressed this by allowing multiple edges per side.
In this model, one edge can exit a side without bending (the center edge), while the others bend slightly away from it, those on the left side bend left, and those on the right bend right. This approach allows for higher-degree nodes while maintaining the orthogonal structure and explains some of the bending behavior you might observe in such diagrams.

Crossing minimization
The process begins with an arbitrary input graph. In the first step, the algorithm fixes the topology. This means it places nodes on the plane and determines the order in which edges leave each node, creating a rough layout. From this, it can identify edge crossings. The goal here is to minimize crossings, which is done through an optimized algorithm. Any remaining crossings are replaced with dummy nodes so that the resulting graph can be processed without any actual edge overlaps. If the input graph can be drawn without crossings, the algorithm will produce such a layout.

Bend minimization
Next is the shape step, where the structure of each edge is defined. The algorithm determines which segments are horizontal or vertical and where the bends occur, but not yet how long each segment should be. At this point, it also aims to minimize the number of bends, keeping the visual structure as simple as possible.

Compactness optimization
Finally, in the coordinate assignment step, the layout engine assigns exact positions to all nodes and edges on a grid. It determines the lengths of edge segments and ensures the drawing is as compact as possible by minimizing the width and height of the diagram.
Concepts recap
| Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Grid placement | Nodes and edge segments are aligned to invisible grid lines, ensuring horizontal and vertical arrangement. |
| Kandinsky model | Allows multiple edges per node side while maintaining orthogonal constraints by assigning bend directions. |
| Crossing minimization | Reduces the number of edge crossings to improve readability in dense diagrams. |
| Bending minimization | Minimizes the number of bends in edge paths for a cleaner, more structured appearance. |
| Compactness optimization | Produces the smallest possible diagram area by tightly packing nodes and minimizing unused space. |
Watch the full webinar episode
Watch the full episode below to gain a comprehensive understanding of orthogonal layouts in yFiles. Dr. Benjamin Niedermann walks you through the core concepts and provides practical demonstrations.
Explore more resources:
Watch the full episode below to gain a comprehensive understanding of orthogonal layouts in yFiles. Dr. Benjamin Niedermann walks you through the core concepts and provides practical demonstrations.

Explore more resources:
Interactive orthogonal layout demos
Discover a selection of interactive demos showcasing different orthogonal layout features in yFiles. Explore how various layout options help visualize complex structured data clearly and intuitively.
Step-by-step guideHow to create an orthogonal layout with yFiles
Creating an orthogonal graph layout with yFiles takes just a few steps:
1. Create the network from business data
2. Make information visible
3. Improve arrangement
4. Apply different layout options

Interactive orthogonal layout playground
The Playground lets you experiment with yFiles' orthogonal layout interactively. Create, edit, and style graphs, adjust layout parameters, and see results instantly—all in one online IDE. Discover how easy it is to prototype and design graph-based applications with yFiles.
graph.nodeDefaults.size = [70, 70];
graph.nodeDefaults.style = new ShapeNodeStyle({
shape: ShapeNodeShape.ELLIPSE,
cssClass: "node",
});
graph.nodeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "white",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid #6A8293",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "#6A8293",
});
graph.edgeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "#6A8293",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid white",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "white",
});
graphComponent.fitGraphBounds()Why use yFiles' orthogonal layout?Unique capabilities for orthogonal layouts you won’t find in other SDKs.
While many software development kits (SDKs) can generate orthogonal layouts, only yFiles provides these game-changing advantages, like grid-perfect positioning, and crossing minimization:
Ideal for diagrams requiring strict alignment, clear spatial relationships, and compliance with engineering or regulatory standards, this layout eliminates diagonal connections and visual noise. It also supports hierarchical clustering to group related elements naturally.
All of this runs efficiently on yFiles’ robust engine, capable of handling thousands of nodes with smooth, real-time layout updates and animations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recap
Orthogonal layout

Orthogonal layout is a specialized graph visualization technique that arranges nodes and edges along horizontal and vertical lines, ensuring all connections follow clean right angles. This approach excels in technical diagrams where clarity and structure are paramount, such as UML, and flow/activity diagrams, circuit schematics, and CAD-like visualizations.
The yFiles SDK offers a robust orthogonal layout engine that creates professional, grid-based diagrams automatically. With advanced features—such as customizable grid placement, Kandinsky model multi-edge routing, crossing and bend minimization, and real-time, animated updates—yFiles’ orthogonal layout adapts to any diagramming need. As detailed in core principles, use cases, and key benefits, yFiles integrates easily into various technical applications, allowing developers to leverage high performance and fine-grained customization across platforms.
To learn more or implement your own grid-perfect diagrams, explore the sections on about the layout, step-by-step guide, or try out live examples.
Related content
Got questions about
the orthogonal layout?

Email: hello@yworks.com
Phone: +49 7071 9709050



