Visualizing Triple StoresGain insights into your RDF/N-TRIPLES/SPARQL database relationships through diagram visualizations
Visualizing graph databases like RDF Triple Stores unlocks powerful ways to understand and analyze complex data structures. With yFiles for HTML, you can transform your RDF/SPARQL data into interactive and insightful diagrams. By visualizing Semantic Web data, businesses can achieve greater data relationship optimization, reduce analysis inefficiencies, and improve data-driven productivity, making it an essential tool for knowledge graph mapping and database process automation. These visualizations allow you to discover relationships and patterns that remain hidden in raw data. Whether you're exploring data, developing applications, or building dashboards, yFiles provides the tools to fully leverage the potential of your RDF/SPARQL data.
Powerful Graph Visualizations for RDF/SPARQL with yFiles
yFiles gives you the tools to create clear and scalable graph visualizations for your RDF Triple Store database. With advanced automatic layouts, you can focus on analyzing and optimizing your graph data instead of arranging nodes manually.
Leverage interactive features, animations, and flexible styling to build dynamic graph applications. yFiles seamlessly integrates with web technologies, making it easy to bring SPARQL/RDF data to life in any application.
Start visualizing your RDF/SPARQL graphs with yFiles today!
Prototype your own graph application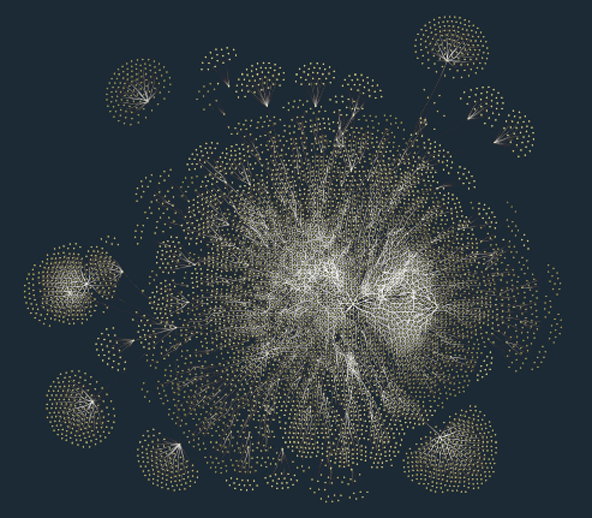
We´d love to help you. Reach out and we'll get in touch with you.
Your message has been sent.
What is RDF/SPARQL?
RDF (Resource Description Framework) is a standard model for data interchange on the Web. It is optimized to store large, connected datasets as triples (Subject-Predicate-Object) in a graph structure, often called a Triple Store or RDF store. It uses SPARQL as its query language, supporting complex pattern matching and joins across linked data. As such, it is perfectly suited for storing and querying large amounts of connected data, especially in the context of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs. When relationships between entities are crucial, a graph database like a Triple Store is essential for understanding and managing complex data structures.
Creating a graph visualization from RDF/SPARQL data
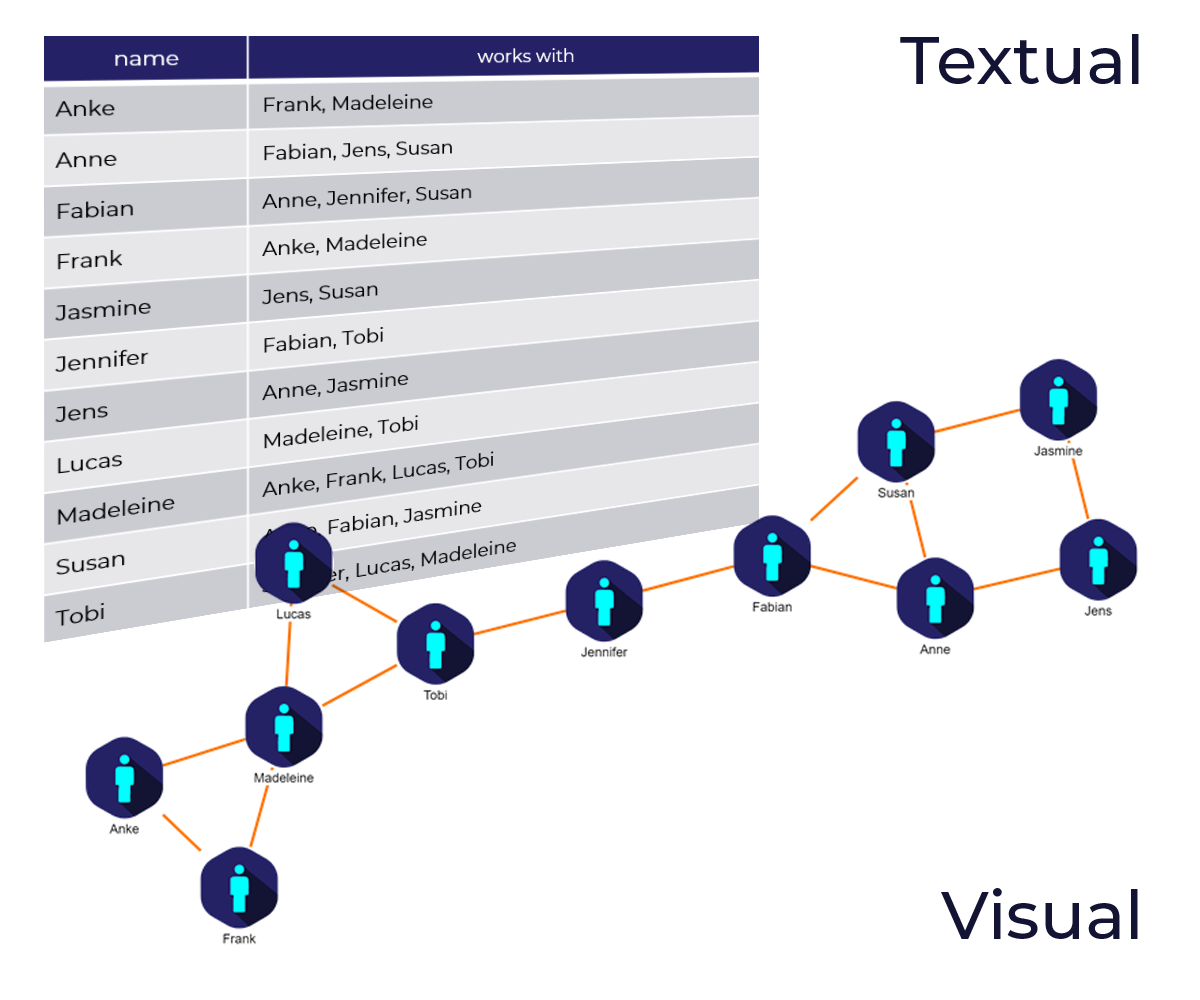
A visualization enables users to visually explore the stored data, identify significant structures, and get a better understanding of relationships. Besides the visual exploration, it is also possible to interactively edit the stored data by modifying the diagram without any SPARQL knowledge, which enables non-technical users to explore and modify the data. For example, new nodes and relationships can be created using mouse gestures. Therefore, visualizing a graph database is a powerful solution when handling or analyzing vast amounts of data.
SPARQL endpoints often provide basic web interfaces or are queried via tools like Fuseki or Virtuoso. This tool lets you run SPARQL queries and displays the result either as a table or in a simple diagram. While this is useful to learn SPARQL and as a quick check if a query returns the right result, more complex tasks often require a sophisticated and customized visualization. Moreover, these basic browsers are mostly targeted at database developers and administrators. It’s not meant to be used by end-users and does not allow for an integration in sophisticated apps and dashboards.

Visualizing RDF/SPARQL data with yFiles
yFiles for HTML is a commercial programming library explicitly designed for diagram visualization and is a perfect fit for the challenges of Semantic Web and graph database visualization. Its sophisticated layout algorithms can easily transform the data into a readable, pleasing, and informative network. With it, you can specify exactly what elements you want to see from your database, how they are represented, and how you can interact with it. It is possible to come up with bespoke interfaces with a great user-experience that perfectly matches the requirements of the end-user:
- Specify what information is loaded from the database (e.g., using
CONSTRUCTorSELECTqueries) - Determine how the elements in the database are mapped to the visualization, e.g. whether to show transitive relationships or even whether to render relationships as connecting arrows or nested hierarchic graph structures
- Create custom designs for your entities to show exactly the information your users are interested in, right in the visualization. Use dynamic icons, progress-bars, gauges, images, colors, interactive elements, text labels, etc. for your item visualizations and level of detail visualizations to keep the visualization both clutter-free and informative at the same time
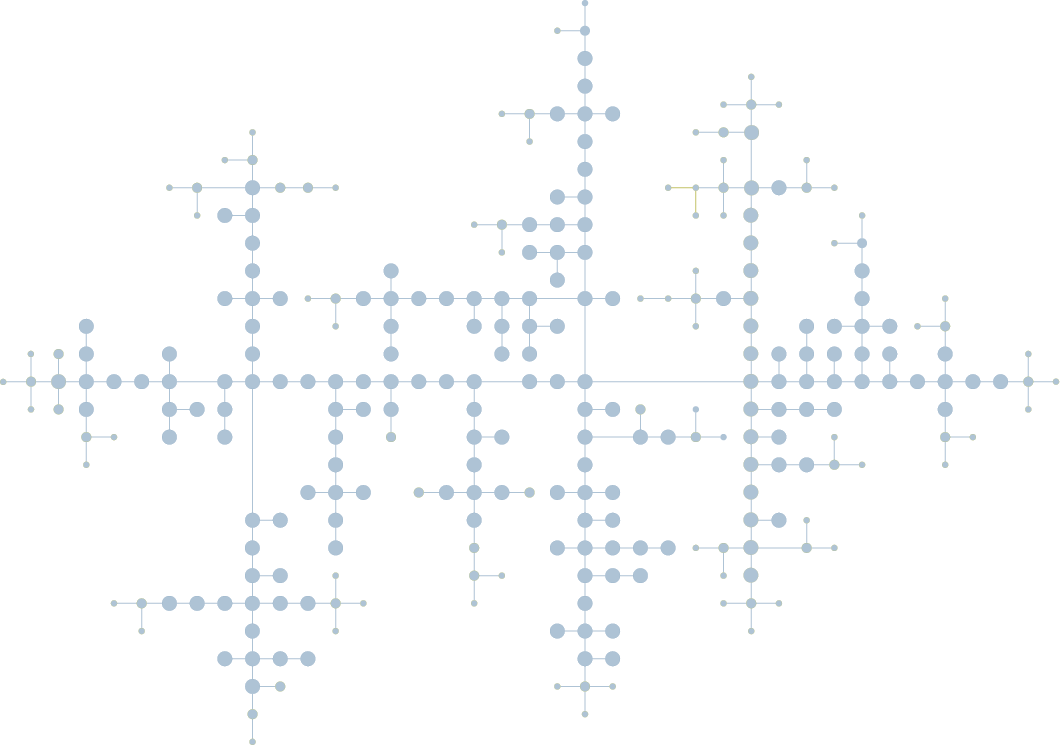
- Use data-driven layouts to highlight important aspects and structures in your data. The different layout styles, for example, hierarchic, organic, tree, circular, or radial, enable the user to intuitively identify structural characteristics of the data, such as hierarchy, connected components, or rings.
- Incrementally load more data, aggregate and group elements, and smoothly animate between these states
- Enable interactivity to let the user interact with the data both for exploratory purposes and to enable live modifications
Connecting yFiles for HTML with RDF/SPARQL
There are different ways to connect yFiles for HTML to an RDF Triple Store data source. Depending on the type of application you can choose between multi-tier architectures where the application connects to a mid-tier level that possibly abstracts away the graph database access. For this, yFiles for HTML allows you to connect to any data source that you can access from the browser: Use REST APIs, SPARQL endpoints, GraphQL endpoints, SOAP, JSON, or even custom binary protocols. Whichever technology allows you to get your hands on the data in the browser can be used for driving the visualization.
On the other hand, you can also directly connect to the database without a complex server setup:
RDF Triple Stores often expose a standard SPARQL Protocol endpoint, which allows you to send SPARQL queries (e.g., using fetch or a dedicated library like rdflib.js or SPARQL-client) directly from JavaScript and Typescript code to the database.
In return, you get JavaScript objects containing the triples you queried from the database.
yFiles for HTML comes with a Graph Builder, which transforms the raw data (triples) resulting from a SPARQL query into a graph structure. After building the graph structure, the full power of the yFiles diagramming library is at your disposal.
Data-driven visualization
A good visualization provides insights into the data that are not obvious by looking at the raw data. yFiles for HTML offers several ways to use the data from the RDF Triple Store to create a rich and meaningful representation. The user can take advantage of the powerful data binding capabilities to create item templates that utilize the predicates and objects (properties) of the RDF triples.

Automatic arrangement
Automatic layouts can give you different perspectives on your data structure. In particular, they make it easy to identify substructures in your data like connected components, chains, circles, stars, and hierarchies. yFiles for HTML provides an extensive set of sophisticated, highly configurable automatic layout algorithms that arrange your data in a clear, concise, and readable manner in the blink of an eye.




Visual representations of different graph structures
Powerful exploration
An interactive application can provide much more functionality than a simple static representation. With yFiles for HTML, a graph visualization can be augmented with a considerable set of interactive features:
- Grouping lets you combine similar or related items to reduce visual complexity
- Drill down helps to explore specific parts of the data
- Filtering can be used to reduce the number of displayed entities without any additional database queries
- Data exploration and interactive modification is possible by mouse, keyboard and touch gestures
- Animations can help to provide a pleasant user experience
About yFiles: The graph visualization SDK
yFiles is your go-to SDK for crafting advanced graph visualizations, whether you're working with Web, Java, or .NET technologies. Its unmatched flexibility and scalability enable you to convert complex data into clear, actionable visuals, fitting for both enterprise and startup needs.
With yFiles, you're equipped for the future—supporting any data source while maintaining strong data security. Getting started is seamless, thanks to over 300 source-code demos, thorough documentation, and direct access to core developer support. These resources are available even during your free trial.
Backed by 25 years of graph drawing expertise, yFiles is trusted by top companies worldwide for their most critical visualization tasks.
Discover yFiles11 reasons why SPARQL developers trust yFiles!

yFiles Newsletter
Stay informed about yFiles, network visualization, and graph technology updates.
Join our newsletterVisualizing SPARQL query results in Jupyter Notebooks
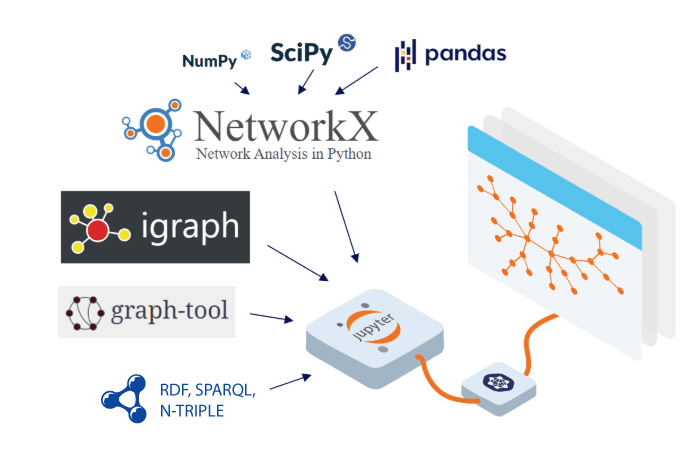
If you are working with RDF/SPARQL graph data as a data scientist with Jupyter Notebooks or Jupyter Labs, consider giving this free visualization plugin a try. yFiles Graphs for Jupyter is a generic graph visualization plugin that can be installed in Jupyter Notebooks to visualize graph data. It comes with support for RDF and SPARQL query results and is the quickest way for data scientists to get started with graph visualization in Jupyter.
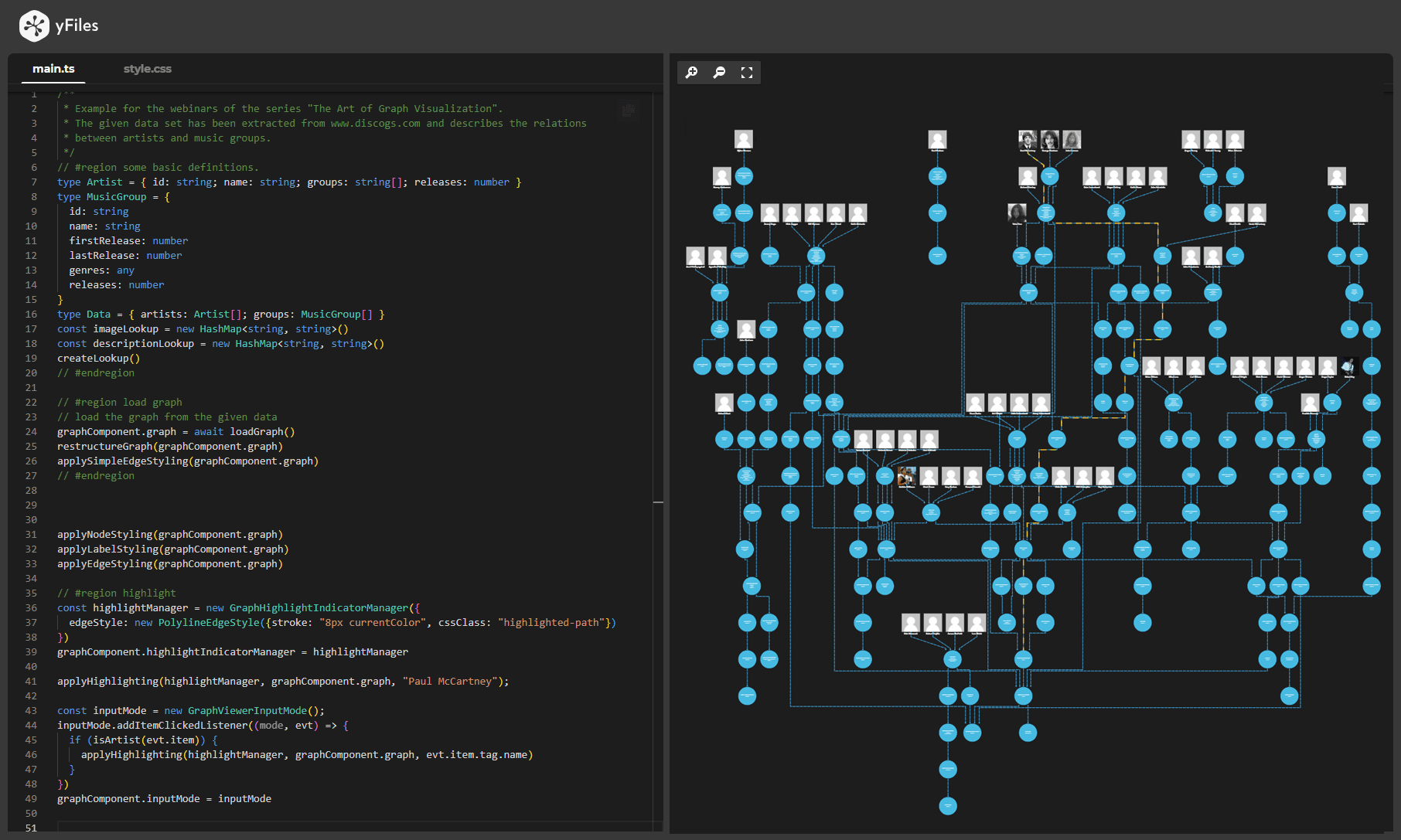
Webinar: How to visualize database content with yFiles
This webinar demonstrates how to visualize a Neo4j database with yFiles for HTML in a simple web application built with JavaScript:

More information is also available in this blog post.











