The Most Complete Layout Selection—for Any Use Case—with yFilesyFiles features: Automatic layouts
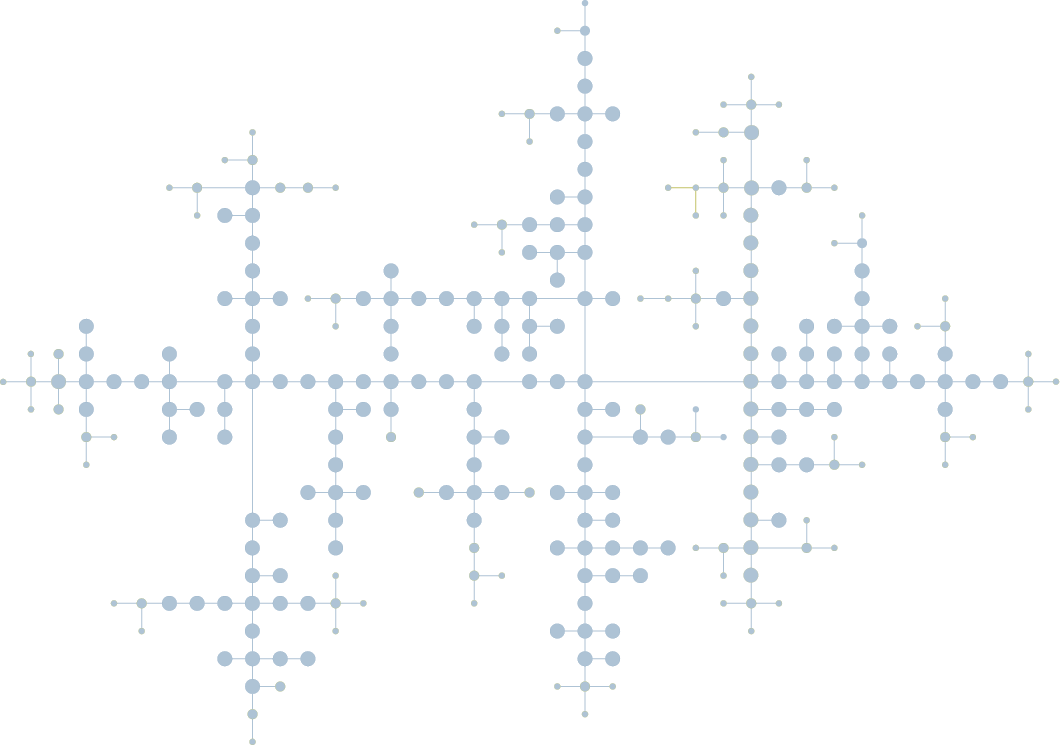
yFiles features efficient and highly customizable algorithms for automatic layouts. The different layout styles are responsible for determining the locations of all diagram elements based on different optimization criteria. A variety of layout styles are included: Hierarchic, organic (force-directed), tree, orthogonal, circular, radial and series-parallel. All layout algorithms can be applied to a diagram in an animated fashion. Almost all aspects of each layout algorithm can be customized to fit a specific domain and use case.
Create interactive diagrams with yFiles, the network visualization library
The yFiles diagramming library supports every step, whether exploring its capabilities for the first time or developing a complete prototype. With hundreds of source-code demos available, getting started or diving into specific use cases is straightforward. Expert guidance from core developers ensures that challenges can be addressed efficiently.
Start visualizing complex networks and dynamic relationships today with yFiles!
Test yFiles free of charge
We´d love to help you. Reach out and we'll get in touch with you.
Your message has been sent.
Hierarchical Layout
The hierarchical layout style arranges nodes in layers so that most edges point in the main layout direction. This layout effectively highlights dependencies and relationships between nodes within a diagram. Consequently, it is well-suited for workflow visualization, process visualization, call-graph visualization, entity-relationship diagrams, biochemical pathways, network management, and swimlane diagrams.
Organic Layout
The organic layout style uses a force-directed approach to distribute nodes in a natural way. This layout uncovers clusters and symmetries in the diagram. It works well for large networks in bioinformatics, enterprise networking, social network graphs, mesh visualization or system management.
Tree Layout
yFiles supports different layout styles for diagrams that have a tree structure. This can be either an organic-looking style that organizes the tree in a star structure around the root node. Or a highly flexible layout style that arranges a tree in layers.
The layouts are able to reveal possible hierarchic relations within the diagram. They're used to visualize relational data, dataflow analysis, software engineering, bioinformatics and business administration.
View demoOrthogonal Layout
The algorithm produces a compact layout with orthogonal edges and no inherent direction. This enables a clear representation of complex networks. Orthogonal drawings are used in software engineering, database schema representation, system management, knowledge representation, VLSI circuits and floor planning applications.
View demoCircular Layout
Nodes are arranged in circle and star structures to emphasize group and tree structures in a diagram. Circular layouts are used in many areas, such as social networking, network management, WWW visualization, e-commerce and telecommunications.
View demoRadial Layout
The radial layout style arranges nodes in concentric circles. Each child node is placed on a larger circle than its parent node. This layout style is well suited for diagrams with many parent-child relationships. If the graph grows, the circles grow larger as well. It can be applied to visualize social networks, data clustering and in bioinformatics.
View demoSeries-parallel Layout
This layout style arranges certain diagrams into serial and parallel substructures. The compact layout highlights the main direction within directed diagrams. It works well for visualizing electrical circuits, call trees or flowcharts.
View demoyFiles Playground: Automatic Graph Layouts
Automatic graph layouts make organizing your diagrams effortless. Try out different layout algorithms like hierarchic, orthogonal, or radial to see how they automatically arrange nodes and edges for optimal clarity and aesthetics.
graph.nodeDefaults.size = [70, 70];
graph.nodeDefaults.style = new ShapeNodeStyle({
shape: ShapeNodeShape.ELLIPSE,
fill: "#6A8293",
stroke: "2px solid #1C2A35",
});
graph.nodeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "white",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid #5F263D",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "#6A8293",
});
graph.edgeDefaults.style = new PolylineEdgeStyle({
stroke: "2px #38536B",
targetArrow: new Arrow({ type: "triangle", fill: "#38536B" }),
});
// andere farben: #00ADCC, #D4C685, #E56399, #C41C38, #13B579
graph.edgeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "#6A8293",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid #6A8293",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "white",
});
graphComponent.fitGraphBounds()Edge Routing Algorithms
Edge routing algorithms compute suitable paths for edges without moving the nodes at all. In general, the goal is to find the best routes for edges so they do not cross any nodes, if possible. yFiles supports different routing styles such as orthogonal or polyline, orthogonal bus-like and organic.
Orthogonal and Polyline Edge Routing
The algorithm calculates new paths for some or all edges in an existing layout. These paths consist of horizontal and vertical segments with as few crossings and bends as possible. The routing is suitable for electric circuit design, floor planning and navigation maps.
View demoBus Routing
The algorithm bundles edges in very dense diagrams into buses. The paths are calculated so they share as many parts as possible. The result clears up the diagram and makes it easier to follow the edges.
View demoOrganic Edge Routing
This force-directed algorithm routes edges curved around fixed nodes. It can be applied as a post-processing for layout algorithms that produce straight-line edges where edges cross nodes.
View demoCommon Layout Features
Each of the layout algorithms mentioned above is highly configurable individually, but they also share several common features. They can calculate layouts for diagrams containing group nodes or swimlanes and allow for edges to be restricted to enter or exit on specific sides of a node. Incremental layout preserves the user's mental map of the diagram by minimizing changes when elements are added or removed, ensuring the diagram remains as consistent as possible.
Incremental Layout
Keep the mental map of a diagram when inserting new nodes and edges. Certain layout algorithms provide an incremental mode which keeps most of the existing layout the same and inserts other nodes appropriately into this pre-existing layout.
View demoPartial Layout
Partial Layout offers a flexible method to maintain specific parts of a diagram in place while recalculating the layout for selected items and integrating them into the overall diagram. It also allows for applying different layout styles to these fixed parts.
View demoEasy Adjustment of Layout Algorithms
Configure the layout algorithms to meet your specific requirements. Each algorithm offers extensive configuration options to accommodate even the most complex layout needs.
View demoAnimated Layout Changes
Calculate a new layout and apply the results with animation. Easily transition between different layouts by animating the changes in the diagram.
Layout Time Restriction
Restrict the time for layout calculation. Layout algorithms can be stopped after a certain amount of time. They may either complete with a valid but potentially lower-quality layout or abort without producing a result.
Restricted Port Locations
Restrict the direction or even the exact location in which each edge is allowed to connect to a node. Such restrictions can also be easily combined to specify a set of valid port locations that can be chosen by the layout algorithm.
Edge Groups
Edges that connect to the same source or target node can be bundled into an edge group. Edge groups share the first or last few segments, this reduces visual clutter and makes it easier to follow the paths of edges.
Bundled Edges
In some diagrams there can be many edges, especially in closely-packed structures. Edge bundling results in organic-looking edge paths where edges with similar routes are pulled closer together. This approach is commonly used in bioinformatics, social network analysis, telecommunications and fraud detection.
View demoLabel Placement
Most layout algorithms can accommodate labels on nodes and edges, reserving space to place them near their corresponding elements without causing overlaps. If that approach is not possible, a generic labeling algorithm can be used. Similar to edge routing, which only changes edge paths without modifying anything else, labels are then placed according to the provided settings in a separate step without changing node locations or edge paths.
View demoGrouped Graphs
When the diagram contains group nodes, then those should not overlap and their contents should be placed closely together so that they still appear visually grouped. Most layout algorithms support placing group nodes according to those criteria. It is even possible to use different layout styles for the contents of each group.
Tables and Swimlanes
Sometimes processes are best visualized in tables or swimlanes. The hierarchical layout, especially, supports the assignment of nodes to a grid-like structure. Node orders are constrained and complicated edge paths through the rows and columns are avoided.
Automatic graph layouts are just one partCheck out what else can be done with yFiles
yFiles provides rich visualizations for nodes, edges, labels, and ports along with options for styling selection and highlighting. If the desired visualization is not covered by the default ones, you can easily create completely custom visualizations.
yFiles also offers versatile interaction possibilities. Set up a complete diagram editor for creating and editing graphs, with just a single line of code. Of course, everything about the interaction can be extensively customized to your requirements, and if the built-in gestures don't suffice, it's easy to add custom interactions.
yFiles allows you not only to create, edit, display, and arrange graphs. There are also a number of analysis algorithms to determine common structural traits (such as connectivity, cycles, whether a graph is a tree and much more), pathfinding and reachability, clustering and centrality measures, graph traversals and many others.
Recap
Automatic Layouts
 This page introduces yFiles’ comprehensive suite of automatic layout algorithms for network and graph visualization. It begins by highlighting the range and flexibility of layout styles available in yFiles, such as hierarchical, organic, tree, orthogonal, circular, radial, and series-parallel layouts.
This page introduces yFiles’ comprehensive suite of automatic layout algorithms for network and graph visualization. It begins by highlighting the range and flexibility of layout styles available in yFiles, such as hierarchical, organic, tree, orthogonal, circular, radial, and series-parallel layouts.
The next sections present core capabilities for building interactive diagrams, including a live playground for experimenting with layout settings.
The page also covers specialized edge routing algorithms that customize how connections are drawn, and a features section detailing advanced options like incremental and partial layout, layout configuration, animation, port restrictions, edge grouping and bundling, label placement, group nodes, and tables/swimlanes.
Finally, it wraps up by pointing users toward additional yFiles features beyond automatic layouts—such as visualization, interaction, and graph analysis.


